Research on the Informatization Construction of Higher Vocational Colleges under the Background of Big Data
Mooring Rope include polyamide fiber series, polyester, resin series, UHMWPE, etc. The products in terms of structure include 3-ply, 4-ply, 6-ply, 8-ply, 12-plyand 48-ply (double-layer braided) with the diameters ranging between 4mm and 146mm for your option. All mooring ropes have wide range of application with the high strength, low elongation, wearing resistance and anti-corrosion.They are soft, smooth and easy for operation. Meanwhile.
Mooring rope is mainly used in fields of ships and vessels, fishing, loadong and unloading in harbor, power supply construction, petroleum survey, physical exercise wares, antional defense scientific and research etc.
Mooring Rope Mooring Rope,Nylon Boat Mooring Ropes,Pp Mooring Rope,White Mooring Rope,Nylon Mooring Rope Jiangsu Xiangchuan Rope Technology Co., Ltd. , http://www.xcropes.com
In the field of education informatization, with the deepening of the people-oriented service concept, digital campuses are gradually transitioning to smart campuses, and campus informatization is changing from traditional management to service-oriented. Digitization is the premise and basis of wisdom, and wisdom must be involved in intelligent data processing and analysis tools. The development of big data technology has provided new tools for smart decision-making and knowledge mining. Comprehensive campus data is in need of big data as a powerful tool to optimize and analyze all aspects of campus services.
In the new phase of building a smart campus, campus information will be based on the wireless network and the Internet of Things, and computing and storage will transition from the server to the cloud. All kinds of information services are highly integrated and shared, and the one-stop experience is more smooth. Under the technical framework of big data analysis, integrate campus business, accumulate business data, and develop data applications. Make full integration of big data technology and smart campus construction, and establish a humanized campus information service system.
Smart Campus Foundation Platform Construction In 2008, IBM proposed the concept of “Smart Earth†based on the application of a new generation of information technology, and its application in the field of university information technology formed the prototype of “Smart Campusâ€. Regarding smart campuses, there is no unified definition. It is generally believed that smart campuses are the new stage for the development of university informatization and the expansion and promotion of digital campuses. It is based on emerging technologies such as mobile Internet, big data, cloud computing, and the Internet of Things. It aims to provide one-stop, personalized campus services, and integrates digital and physical space on campus. As shown in Figure 1, it is highly efficient. , sharing, flexible, and easy-to-use smart service and management system. 
(1) Improve the wireless network architecture and improve the stability and security of wireless networks.
Expand campus WLAN coverage, improve network carrying capacity, strengthen authentication and security management, and provide a secure and stable network foundation for data collection and exchange.
(2) Improve the three platforms, open up data silos, and establish a collection and exchange center for structured data.
Apply unified campus data standards, strengthen data integration of various business systems, establish complete data collection and maintenance management mechanisms, and transition from single sign-on of multi-service systems to highly integrated digital identities. Guarantee the convenience, effectiveness and timeliness of campus data collection.
(3) Plan data acquisition terminal, integrate existing system monitoring and log resources, and build a distinctive campus social ecology.
Optimize the “one card†system, and on the basis of “multi-card integrationâ€, make “one card†an important bridge for physical personnel and digital space; plan interface standards for data collection terminals such as electronic control, water control, access control, and environmental detection. Spatial distribution; integrates existing data and log resources such as network management systems, network flow control systems, security systems, and standardized examination room monitoring systems, and integrates public social platforms such as WeChat, Weibo, and Post Bar, and campus app platforms to create data centers. Semi-structured and unstructured data exchange centers.
Data-centric campus service fragmentation "smart campus" aims to improve the quality of "services", and good service experience is often associated with personalization, convenience, and efficiency. The data-centric concept of campus service fragmentation will solve the problem of traditional campus business systems in improving service. The so-called "service fragmentation" is to sort out the existing campus business processes and data flow, horizontal integration of the original business system, loose coupling in the business logic, emphasizing an application (called app) only one Pieces of business. For example, the appellation app (see Figure 2) is presented to faculty and staff to complete the completion of a job title review process, including the relevant forms to fill in, upload the information and review the progress of inquiries, etc., as long as teachers follow the guide to complete step by step. And its backstage may involve data updates and audits of personnel systems, educational services, scientific research, and other business systems. The fragmented service shields the user from the business system. Only the concept of transaction greatly enhances the user experience and efficiency of the information system. 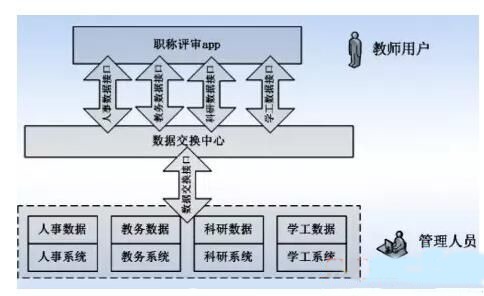
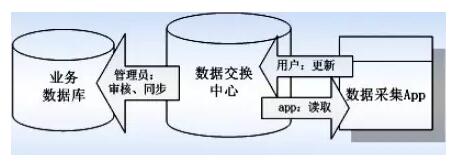
Improving the design of campus data exchange centers to adapt them to fragmented data service interfaces is the focus of the data layer. In the design of the data interface, three layers of design principles are introduced: 1 personal query. Allows individual users to easily query and modify relevant information within the scope of their privilege, and obtain campus information in a timely manner; 2 department department statistics. Department departments can collect, count and analyze the data they are concerned about, facilitate the understanding of the operation of the department, and formulate reasonable measures in time; Within the scope of the school level, more emphasis is placed on the presentation and information mining of the overall data to provide the basis for school-level decision-making.
Campus data applications <br> <br> data applications is an integral part of the "smart campus", but also "wisdom" is an important manifestation. With the accumulation of campus data, the ability to acquire things through big data analysis to improve campus services has also been further enhanced. Regardless of personal, faculty and school level, the acquisition of a large number of information models can be used to guide specific tasks and decisions. The conventional campus data application has the following aspects:
1. Source data analysis According to the registration rate of freshmen in each area and the learning performance at school, adjust the distribution of students and enrollment strategies. In the analysis process, students can be reduced to the county, town, or even the school level for the source of the province, and the source of the analysis can be expanded to provincial or even large areas. According to the analysis results, the enrollment department is instructed to conduct pre-exam lectures and preferential policies, so as to improve the quality of the students' education.
2. Employment data analysis Through the analysis of students' professional distribution and employment data, the structure distribution of students in various specialties and the employment dynamics of graduates are known, and a reasonable information sharing model is explored. The users and my school are more fluent. Information exchange. It is also possible to establish career data tracking for graduates, to better guide the employment diversion of students in school, and to give play to the role of outstanding graduates in vocational guidance for students in school. The employment policy formulated by the school can timely reflect the needs of the job market and improve the social competitiveness of graduates.
3. Campus flow analysis Based on the spatial characteristics of WLAN access distribution and information flow distribution, combined with monitoring information of security systems, real-time tracking and early warning of hotspots and hotspot events within the school. It is also possible to adjust the local network structure and flow control strategy based on the real-time data of access points and traffic at the information point in order to improve the user's network usage experience and make full use of limited network resources.
4. One-card data analysis Through the analysis of one-card consumption data, students' daily dining and life consumption patterns are analyzed, and data basis is provided for work-study, poverty-stricken students, scholarships, grants for scholarship, etc. to ensure that subsidies are paid as reasonably as possible. You can classify students' consumption patterns (consumption time, consumption content). Combine with health data to provide teachers and students with personalized, healthy dietary advice; combine with teaching data to explore the relevance of lifestyle and academic performance.
5. Analysis of teaching data In the teaching data, through the classroom arrangement and arranging system, the school's classroom and laboratory resources are statistically analyzed to provide reference for the optimization of the arranging course in the Office of Academic Affairs; through the teaching and learning system data Integrate, track and count students' class rate and elective information, establish an absenteeship early warning notification system, provide timely warnings or other information feedback to students who regularly skip classes, be late or leave early, and guide students to complete their studies smoothly. It is also possible to analyze the correlation between learning performance (class rate, classroom performance, etc.) and academic performance, so as to help each major to identify key courses and even key courses, reform curriculum settings in time, and improve teaching effectiveness.
6. Internet behavior analysis Through the analysis of network flow control data and access data, tracking different users' surfing habits, access content, and software usage. Assist in the detection of campus trends, technological trends and hotspot events, as well as control and early warning of possible virus and public opinion incidents. You can also analyze correlations with academic performance and health data so that schools can conduct timely training and guidance and guide students to form healthy internet usage habits.
7. Book borrowing data analysis Through the analysis of book borrowing and electronic reading room use data, students' reading patterns and reading frequency, as well as content requirements for digital resources, provide basis for adjusting the types of books and improving reading services. Students can read relevant content, number of readings, borrowing habits, academic status, and performance analysis to better guide students in book reading and book recommendation.
Conclusion <br> <br> wisdom campus around data collection, data analysis and data applications start. In the process of big data applications, there are also many problems. 1 data collection and management mechanism issues. The entry and review of source data is a prerequisite for ensuring data validity, and data security and privacy protection also require a reasonable management mechanism. 2 data source problems. Data applications require a large-scale data base, otherwise it will cause the accidental pattern mining. Insufficient data integrity or the presence of erroneous data may result in invalid pattern mining. 3 mining mode verification issues. The patterns of data mining are not always valuable, and some are even wrong. This requires strict theoretical analysis and practical argument. Data-only theory is not desirable.
In short, the current research and application of big data are still in the preliminary stage, but many experts and scholars have high hopes for "big data technology", and even think that this will open the curtain of "data technology" era. “Wisdom Campus†is the new direction of campus information construction. Big data analysis, as a key technology of “Smart Campusâ€, will have a profound impact on improving campus services and improving campus management. (Author: Xuguan Jun, etc., Taizhou Vocational College of Science and Technology)
