Classification, floatability and flotation process of copper sulfide ore
Many copper-containing natural minerals, industrial value dozen. The main copper minerals for flotation treatment are chalcopyrite, chalcopyrite, copper blue, and porphyrite. Most of the copper ore processed in China is chalcopyrite ore. All copper sulfide ore contains iron ore (pyrite) more or less, so the flotation task of copper sulfide is separated from iron sulfide and gangue minerals to obtain copper concentrate. If the content of iron sulfide is large, it should be recycled at the same time. Copper ore sometimes contains gold , silver , cobalt , nickel, etc., and comprehensive recovery of these symbiotic ore can be considered. 1. Classification of copper sulfide ore The industrial types of copper ore in China are: layered copper ore, fine vein disseminated copper, skarn copper, pyrite copper and porphyry copper. About 60% of the world's copper is currently from porphyry copper ore. The difficulty of copper ore flotation is closely related to the content of iron sulfide in the ore. According to the content of iron sulfide, copper sulfide ore is divided into two types, one is dense brittle copper ore and the other is disseminated copper ore. The former is characterized by high content of pyrite in the ore, sometimes up to 80% to 85%, gangue content is very small, and copper sulfide and iron sulfide minerals are densely symbiotic. The tailings remaining after the ore is selected from the copper sulfide minerals are usually iron sulfide concentrates. If the gangue content is high, the pyrite should be sorted to obtain a pyrite concentrate. The latter's ore body is mainly composed of gangue minerals, and the content of copper sulfide and iron sulfide is low, and it is distributed in the gangue. The majority of our copper ore processing plant is disseminated copper ore. Second, the floatability of copper sulfide ore The most common copper mineral in China's copper ore is chalcopyrite (CuFeS 2 , containing 66.49% copper), followed by chalcopyrite (Cu 2 S, containing 79.83% copper), copper blue (CuS, containing 66.49% copper). ), copper ore (Cu 3 FeS 3 , 55.5% copper). From the perspective of buoyancy, the copper ore and copper blue are the most easy to float. They are all secondary copper mines with very low hardness and are extremely muddy. Chalcopyrite is the most widespread native minerals, flotability or, a typical collector type xanthate, cyanide, it is possible to suppress flotation, heavy chromate, sulfite can not suppress it. The floatability of the porphyrite is between the chalcopyrite and the chalcopyrite. In summary, the floatability of copper sulfide ore has the following rules: 1. Iron-free minerals such as chalcopyrite, copper blue, etc., which are similar in floatability. It is less effective when they are inhibited by cyanide or lime. 2. Iron-containing minerals, such as chalcopyrite and porphyrite, are susceptible to inhibition by cyanide and lime in alkaline media. 3. When harvesting with xanthate, the order of its harvesting capacity is: chalcopyrite > copper blue > porphyrite > chalcopyrite. Since anions and cations mainly xanthate with chemically adsorbed Cu 2+ sky effect collector surface containing Cu 2+ more minerals, and xanthate stronger. 4. The higher the content of oxidized minerals and copper salts, the more difficult it is to sort. This reduces the recovery of copper minerals; on the other hand, it is difficult to separate from iron sulfide. 5. The coarser the particle size of the inlay, the less the slime content, the easier it is to float, and the higher flotation index. Copper sulfide minerals and iron sulfide minerals are densely symbiotic, and the content of slime increases during fine grinding, which causes separation difficulties and deterioration of flotation indexes. 6. The secondary copper mineral itself is buoyant, but Cu 2+ in the pulp is easy to activate other minerals. Secondary copper minerals have a high degree of muddyness, are easily oxidized, cause loss of fine-grained grades, and increase the difficulty of flotation. 7, when the ore contains talc, kaolin, sericite gangue, floating or better, or ease of mud, easily contaminated concentrate is difficult to obtain a high-quality concentrate. Third, the flotation of copper ore There are two options, priority flotation and hybrid flotation. (1) Priority flotation Always float copper first, then float sulfur. The collector can be used with xanthate or with black medicine. For dense massive copper-bearing pyrite, in order to suppress a large amount of pyrite during floatation, it should be carried out in a strong alkaline medium with a pH of 11-12, and the free CaO in the slurry is controlled at about 700 to 1000 g/L. For disseminated ores with low pyrite content, copper ore flotation can be carried out at pH=8-9. (2) Mixed flotation Copper-sulfur mixed concentrate is usually selected from a neutral medium with a pH of about 7 to 8. The free CaO in the slurry is controlled at about 100 to 150 g/L. The copper-sulfur mixed concentrate is then separated. The separation of mixed concentrates has a lime method: 1. Lime method - increase the pH of the medium to make it alkaline and inhibit pyrite. 2. Lime plus cyanide method - used when pyrite has high activity and is not easily inhibited by lime. 3. Heating method - used for copper-sulfur mixed concentrate which is difficult to separate to accelerate the surface oxidation of pyrite. The above copper-sulfur separation method can also be used for preferential flotation of copper. 4. Examples of flotation of copper ore (1) Flotation of disseminated copper ore Generally, a relatively simple process is adopted. After a period of grinding, the fineness-200 mesh accounts for about 50% to 70%, one rough selection, two to three times, and one or two sweeps. If the particle size of the copper mineral is relatively fine, a stage grinding process may be considered. Most of the concentrating plants that deal with the porphyrite mine use the coarse concentrate regrind-selected stage grinding process, which is essentially a mixing-priority flotation process. After a rough grinding, rough selection, sweeping, and then re-grinding the coarse concentrate to obtain high-grade copper concentrate and sulfur concentrate. Rough grinding fineness - 200 mesh accounts for about 45% to 50%, and regrind fineness - 200 mesh accounts for about 90% to 95%. (2) Flotation of dense copper ore Dense copper ore Due to the dense symbiosis of chalcopyrite and pyrite, pyrite is often activated by secondary copper minerals. The content of pyrite is high, it is difficult to suppress, and sorting is difficult. Copper concentrate and sulfur concentrate are required to be obtained simultaneously during the sorting process. The tailings usually selected after copper are sulfur concentrates. If the gangue content in the ore exceeds 20% to 25%, it is necessary to sort again to obtain the concentrate. For the treatment of dense copper ore, two-stage grinding or stage grinding is often used, and the fineness of grinding is required to be fine. The dosage of the drug is also relatively large, and the amount of the yellow drug is 100 g/(t ore) or more, and the lime is 8 to 10 kg/(t ore) or more.
Product description:
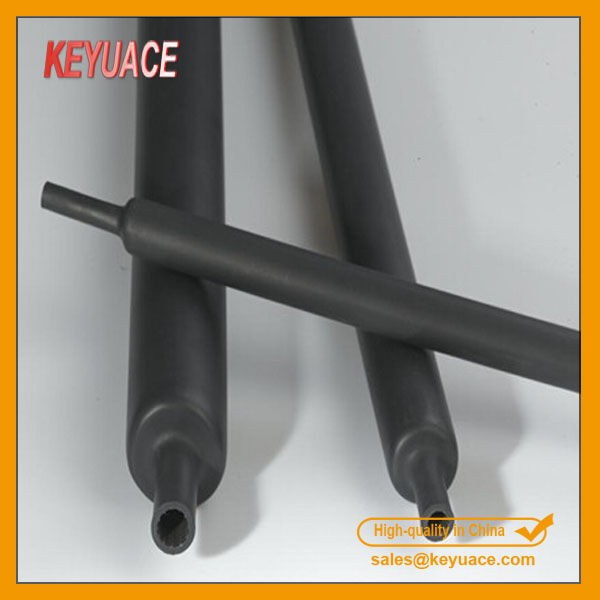
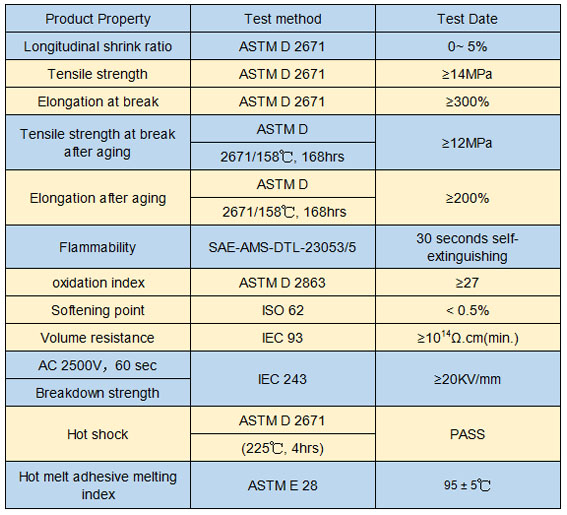
HJT-FR Flame retardant heavy wall adhesive-lined heat shrink tubing is made of the outer layer flame retardant polyolefin PE material and the inner hot melt adhesive layer, and it has flame-retardant and high insulation properties. Heavy Duty heat shrink tubing it's mainly used to the connector of the middle and end of the high-voltage wire, shipping electric wire, binding wire and metal conduit for insulation protection and other pipeline for anti-corrosion and wear proof.
Feature & benefit:
a) Heat shrink ratio: 3/1, flame-retardant outer layer
b) Anti-UV, anti-irradiation, damp proof, waterproof, sealing
c) Efficient electronic insulation protection, superior mechanical protection performance
d) Standard colors: Black, red
Operating indexes:
a) Min. Shrink temp.: 100 degrees Celsius
b) Final shrink temp.: 120 degrees Celsius
c) Working temperature: -55~110 degrees Celsius
Up to standard: Approvals
Meet ROHS environmental protection, 110 degrees CCelsius.
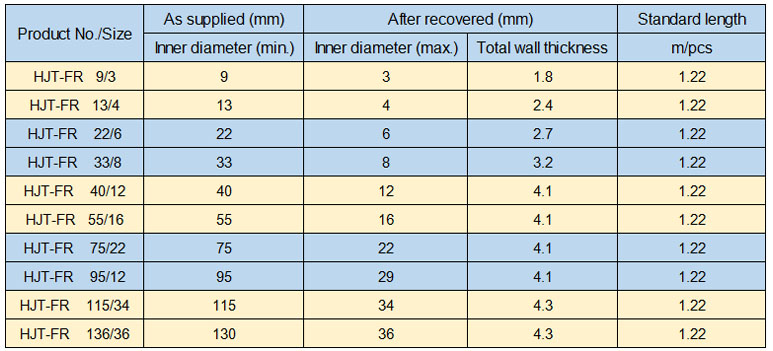
Product specification:
Heavy Duty Tubing,Construction Heavy Duty Tubing,Flexible Heavy Duty Tubing,Polyolefin Heavy Wall Heat Shrink Tubing,Heavy Wall Heat Shrink Tubing KEYUACE Materials Co., Ltd. , https://www.insulationtubing.com
HJT-FR Flame retardant heavy wall adhesive-lined Heat Shrink Tubing